When exploring the realm of electronics, the term IR Sensor frequently emerges as a topic of interest. What is an IR sensor, exactly? In simple terms, it’s a device that uses infrared technology to detect and measure certain aspects of its environment. An IR sensor emits or receives infrared radiation and then translates it into an electrical signal. This technology is fascinating and widely applicable in various fields, from robotics to home security systems.
Moreover, the IR sensor price is quite affordable, making it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike. People often use IR sensors interchangeably with their full form, Infrared Sensor, to reflect their ability to detect infrared radiation. This versatility and cost-effectiveness have made IR sensors popular in numerous applications. You can check our other article about IR Sensor Working Principle and Applications on our website.
Introduction
Delving into the world of IR sensors, it’s essential to understand the basics of this technology. An IR sensor module is a compact assembly with the necessary components to detect infrared radiation. These modules are integral parts of many electronic devices, allowing them to sense and interact with their surroundings.

IR sensors are not just limited to complex machinery but also everyday gadgets. The IR sensor module plays a crucial role, from the simple remote control that changes your TV channels to sophisticated systems that help cars navigate. Its widespread use is a testament to its reliability and efficiency in various applications.
What is IR Sensor
An IR sensor, or Infrared Sensor, is a device that detects and measures infrared radiation in its environment. This sensor operates on the principle that all objects emit some form of infrared radiation as a function of their temperature. The IR sensor detects this radiation and converts it into an electrical signal.
This technology is incredibly versatile. You can use it to measure heat emitted by objects or even detect motion. For instance, in a security system, an IR sensor can detect the presence of a person by the infrared radiation emitted by their body. Furthermore, these sensors are integral in applications like touch-free interfaces, where they see hand movements and gestures.
In conclusion, grasping IR sensor basics unlocks potential for practical and innovative uses across various fields. The IR sensor’s affordability and versatility are essential for anyone passionate about electronics and technology. Its diverse applications and system integration make the IR sensor crucial in technological advancement.
Working of an IR Sensor
The IR sensor working principle is a fascinating aspect of modern technology, offering a window into how these devices interact with their environment. Essentially, the IR sensor working method involves detecting infrared radiation, which is invisible to the naked eye but crucial for various applications. At the heart of the IR sensor working principle is a simple yet effective mechanism: an IR LED emits infrared light, and an IR photodiode, sensitive to this light, acts as the receiver.

When the IR light hits the photodiode, it alters its resistance and output voltage in proportion to its intensity. This change is what the sensor interprets, making the IR sensor working principle a cornerstone in fields ranging from automation to security. Understanding the IR sensor working process is not just about grasping the technicalities; it’s about appreciating how these sensors have become integral in our interaction with technology, transforming how we perceive and respond to our surroundings.
How does an IR sensor work?
The fundamental operation of an IR sensor revolves around an IR LED and an IR Photodiode. These two components form a crucial duo, working to detect infrared light. The IR LED emits infrared radiation, while the IR Photodiode acts as a receiver, sensitive to the LED’s emitted IR light. When infrared light strikes the photodiode, it changes its resistance and output voltage, proportional to the intensity of the IR light received. This change is what the sensor interprets to provide valuable data.

Furthermore, the IR sensor’s functionality is more comprehensive than detecting objects’ presence or absence. It can also gauge the object’s distance, size, and other attributes. This versatility makes the IR sensor module popular in various fields, from robotics to security systems.
IR Proximity Sensor Working Principle
The IR Proximity Sensor, a specific type of IR sensor, operates on a principle similar to the general IR sensor but focuses on proximity detection. It uses an IR LED to emit light and a photodiode to detect the reflected IR light from nearby objects. The photodiode determines the proximity of the object based on the intensity of the reflected light it receives. The closer the object, the stronger the reflected signal, allowing the sensor to gauge proximity accurately.
Moreover, the IR Proximity Sensor is adept at differentiating between an object’s presence and absence within a specific range. This feature is particularly useful in applications like automated lighting systems, where the lights turn on or off depending on whether someone is in the room.

In conclusion, IR sensors, including the IR Proximity Sensor, showcase remarkable progress in sensor technology. Their capacity to detect and measure infrared radiation revolutionizes automation, security, and robotics. Grasping the workings of IR sensors reveals their crucial role in our tech-centric world. IR sensors’ applications will expand as innovation progresses, solidifying their importance in future technology.
Advantages of IR Sensor
IR sensors are a notable technological innovation, providing numerous advantages across diverse applications. These infrared technology sensors have revolutionized how we interact with machines and environments.

Ease of Integration and Cost-Effectiveness: One of the most significant advantages of IR sensors is their affordability and ease of integration. These sensors seamlessly integrate into both small projects and large industrial applications, appealing to businesses and hobbyists. Their simple design and low power consumption further enhance their appeal, allowing for long-term, cost-effective solutions.
Versatility in Applications: Another crucial benefit of IR sensors is their versatility. These sensors are used in various applications, from home security systems to industrial automation. They are adept at short-range sensing and long-distance operations, making them incredibly flexible for multiple uses.
Rapid Response and Reliability: Regarding speed, IR sensors are unmatched. Their ability to transmit high-frequency waves quickly and over large distances without interference ensures a rapid and reliable response. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications where quick detection and reaction are crucial.
Environmental Resistance: Another notable advantage of IR sensors is their resilience to environmental factors like wind pressure changes. This makes them suitable for indoor and outdoor applications, even in challenging weather conditions like rain or snow.
Energy Efficiency: IR sensors consume considerably less power than other technologies like ultrasonic sensors. This feature greatly extends the operational duration of battery-powered devices like autonomous robots and drones, reducing frequent battery changes.
Compact Design: IR sensors’ compact size and sleek design enable their use in tight spaces, ideal for space-limited applications. This has made them a favored choice in consumer electronics, where adherence to compact design specifications is often critical.
Disadvantages of IR Sensor
Despite their numerous advantages, IR sensors also have certain limitations that need consideration.

Susceptibility to Interference: IR sensors often struggle with external heat sources like sunlight, causing unreliable or inaccurate readings. Outdoor environments or areas with fluctuating light intensify this issue, significantly impacting sensor reliability.
Limited Range and Obstruction Issues: IR sensors have a limited range, often needing help with accuracy over long distances or through obstacles. This shortcoming affects applications requiring comprehensive coverage or facing barriers in the sensor’s view.
Humidity Sensitivity: High humidity levels can adversely affect the performance of IR sensors, potentially leading to false positives or other inaccuracies. This sensitivity makes them less suitable for use in fluctuating or high-humidity environments.
Durability Concerns: Continuous exposure to varying temperatures can accelerate the aging of IR sensors, affecting their reliability and accuracy over time. This is particularly problematic in outdoor settings or climates with extreme temperature fluctuations.
Types of IR Sensors
In infrared technology, IR sensors are a cornerstone, offering diverse applications. Broadly categorized into two types, Active and Passive, these sensors precisely cater to various needs. Active IR sensors, which include both a transmitter and receiver, excel in applications requiring direct object detection, such as security systems and automated doors.
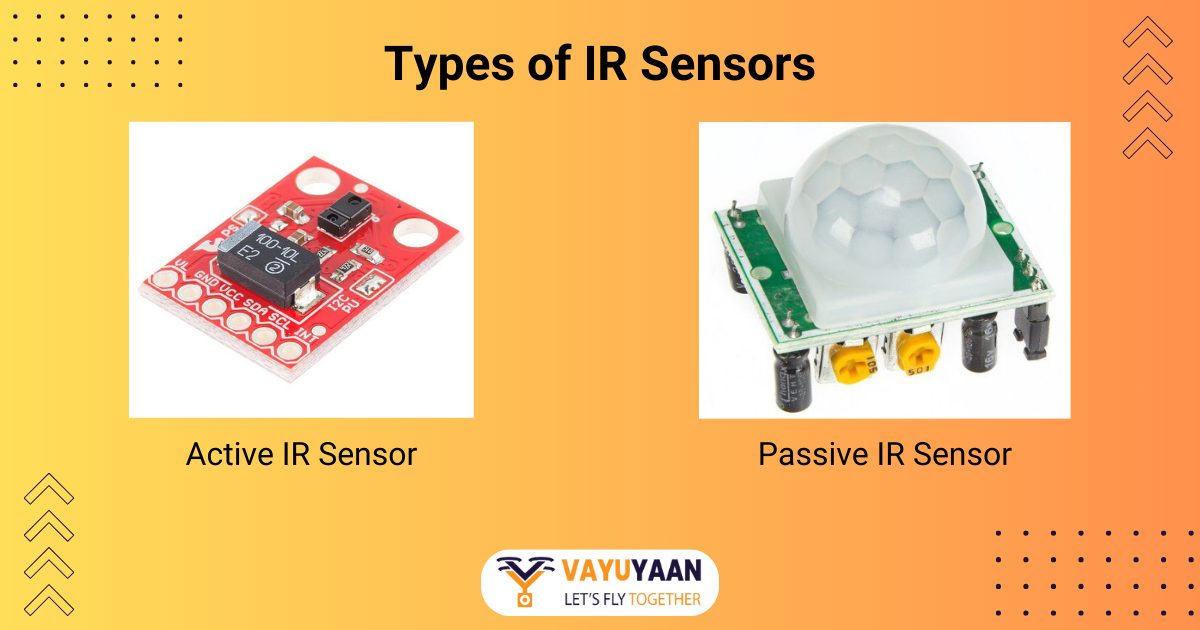
On the other hand, Passive IR sensors, which operate without an emitting component, are adept at detecting the presence of living beings through their natural infrared emissions, making them ideal for applications like motion-activated lighting and intruder alarms. Within these categories, further specialization exists in thermal infrared sensors, which detect heat emissions and are invaluable in thermal imaging, and quantum infrared sensors, known for their high sensitivity and used in more specialized fields like spectroscopy. Each type of IR sensor, whether active or passive, thermal or quantum, plays a unique role in its respective domain, showcasing the versatility and indispensability of IR sensor technology in modern applications.
Active IR Sensor
Active IR sensors are dynamic components in infrared technology. They consist of a transmitter and a receiver, working in tandem to detect objects and movements. Typically, these sensors employ a light source such as a laser diode or LED. The active IR sensor emits energy, and the detector captures it. This interaction is crucial for obtaining vital data, making active IR sensors indispensable in applications like reflectance and break beam sensors.

The beauty of active IR sensors lies in their versatility. They can be used in various environments, from industrial settings to everyday consumer electronics. Their ability to accurately detect presence and movement makes them popular for security systems, automated doors, and even robotics.
Passive IR Sensor
Shifting our focus to passive IR sensors, these devices operate without an active transmitter. Instead, they rely on detecting the infrared energy emitted by nearby objects. This makes them particularly effective in applications where the goal is to sense the presence or absence of humans or animals, as these living beings naturally emit infrared radiation.

Passive IR sensors are commonly found in security systems and motion-activated lighting. Their ability to operate without emitting radiation makes them energy-efficient and unobtrusive, ideal for use in environments where discretion is critical.
Thermal Infrared Sensor
Diving deeper into the types of passive IR sensors, we encounter the thermal infrared sensor. These sensors are unique in that they are wavelength-independent. They detect heat emitted by objects, making them respond slower but highly effective in specific scenarios. Users widely employ thermal infrared sensors in applications requiring the detection of heat signatures, including thermal imaging cameras and temperature sensors.

Thermal infrared sensors find versatile applications across different domains. In the realm of medical diagnostics, these sensors play a crucial role by aiding in the detection of fever or inflammation. Similarly, they serve as vigilant guardians in industrial environments, continuously monitoring machinery temperatures to prevent potential overheating issues.
Quantum Infrared Sensor
Quantum infrared sensors represent the cutting edge of IR sensor technology. These sensors are wavelength-dependent and are known for their quick response times and high detection accuracy. They require periodic cooling to ensure precise measurements, making their operation slightly more complex than thermal sensors.

Quantum infrared sensors find their use in highly specialized applications, such as spectroscopy, where they help identify different materials based on their infrared signatures. Astronomers also use them to detect celestial objects not visible in the regular light spectrum.
Applications of IR Sensors
In the dynamic world of technology, the applications of IR sensors are both varied and fascinating, making them integral components in numerous fields. These sensors, known for their ability to detect and measure infrared radiation, have revolutionized how we approach everyday tasks and complex challenges. From enhancing home security systems with precise motion detection to enabling smart energy management through automated lighting controls, the versatility of IR sensor applications is genuinely remarkable. In industrial settings, they streamline processes by accurately counting products on assembly lines, while in healthcare, they offer non-invasive monitoring of vital signs. Even in the realm of entertainment, IR sensors are the unsung heroes behind the seamless operation of remote controls. IR sensors’ diverse uses emphasize their role in crafting a more efficient, connected world. Their growing impact on technology advancement and daily life enhancement is clear, solidifying their importance in the evolution of smart systems.

Proximity Sensor
One of the most common uses of IR sensors is proximity sensing. These sensors are adept at detecting the presence or absence of objects without any physical contact. For instance, in smartphones, IR sensors play a crucial role in turning off the screen when you hold the phone close to your ear during a call. This not only saves battery life but also prevents unintended touches. The principle behind this is straightforward yet ingenious: the sensor emits infrared light, which bounces back upon hitting an object nearby, signaling its presence.
Item Counter
IR sensors play a vital role in the industrial sector and are particularly invaluable for counting items on production lines. This application underscores the sensor’s precision and reliability. As things seamlessly pass between the IR transmitter and receiver, the system promptly registers any interruption in the infrared beam as a count. Manufacturers extensively employ this method for efficient inventory management and rigorous quality control. Consequently, this ensures accuracy and heightened efficiency in high-volume production environments. Moreover, this seamless integration of IR sensors enhances productivity, streamlines operations, and minimizes errors in the industrial workflow.
Burglar Alarm
Security systems heavily rely on IR sensors for intrusion detection. When used in burglar alarms, these sensors detect unauthorized movement within a protected area. The sensor emits an infrared beam, and if an intruder interrupts this beam, it triggers the alarm. This application of IR sensors provides a robust security solution for homes and businesses alike, offering peace of mind through enhanced safety measures.
Radiation Thermometers
IR sensors have revolutionized temperature measurement with radiation thermometers. These devices measure the infrared radiation emitted by objects, enabling non-contact temperature assessments. This is particularly useful when traditional thermometers are impractical, such as counting the temperature of moving things or surfaces that are too hot to touch. From industrial furnaces to cooking appliances, radiation thermometers provide a safe and efficient means of temperature monitoring.
Human Body Detection
The ability of IR sensors to detect heat signatures makes them ideal for human body detection. This application is crucial in systems like automatic lighting, where lights turn on or off based on the presence of people. Advanced security systems also use it, where the sensor can differentiate between a human and other moving objects, reducing false alarms and enhancing the system’s effectiveness.
Gas Analyzers
IR sensors are instrumental in environmental monitoring, particularly in gas analyzers. These devices measure the concentration of various gases by detecting each gas’s specific infrared absorption patterns. This application is vital in petrochemicals and waste management industries, where monitoring and controlling gas emissions are crucial for safety and environmental compliance.
Other Applications
The versatility of IR sensors extends to numerous other applications. Furthermore, they are used in remote controls, allowing seamless operation of devices like TVs and air conditioners. Additionally, IR sensors enhance automotive system safety through features like automatic braking and parking assistance. Moreover, even in healthcare, these sensors monitor vital signs and blood flow.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of IR sensors, it’s clear that these devices are not just technological marvels but also integral components in modern automation and security systems. The journey through the world of IR sensors reveals their versatility and efficiency, making them indispensable in various applications.
Firstly, the IR sensor stands out as a beacon of innovation because it can detect and measure infrared radiation. Its applications range from simple proximity detection to complex thermal imaging, highlighting its adaptability in diverse fields. The IR sensor module is essential for smartphones and advanced security systems, boosting their functionality and efficiency.

Moreover, the adaptability of IR sensors is evident in their widespread use. These sensors have revolutionized our interactions with technology, from everyday household appliances to advanced industrial machinery. They offer a seamless, intuitive experience, making our interactions with gadgets and systems more natural and efficient.
It’s also worth noting that IR sensors’ simplicity and effectiveness make them accessible to a broad audience. Their ease of integration into various systems means that even those with minimal technical expertise can harness the power of infrared technology. This accessibility is crucial in a world where technology rapidly evolves and becomes more intertwined with our daily lives.
In conclusion, the IR sensor and its module variant are testaments to human ingenuity and our relentless pursuit of technological advancement. As we continue to innovate and push the boundaries of what’s possible, IR sensors will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping the future of technology. They are components and building blocks of a smarter, more connected world.
Frequently Asked Questions about IR Sensors
Frequently Asked Questions about IR Sensors offers insightful answers to common queries surrounding these versatile devices. From understanding their basic working principles to practical applications, this section demystifies IR sensors, addressing technical and beginner-level questions. Anyone keen on exploring the fascinating world of infrared technology should read it.
What is the working principle of IR proximity sensor?
IR proximity sensors operate on a simple yet effective principle. They emit infrared light, which bounces back upon encountering an object. The sensor detects this reflected light, determining the presence and distance of the object. This mechanism is integral in applications like automatic doors and robotics, making IR sensors a versatile tool in modern technology.
What is the IR sensor?
An IR sensor is a device that detects and measures infrared radiation in its environment. Utilizing the properties of infrared light, these sensors are pivotal in numerous applications, ranging from remote controls to security systems. Their ability to sense heat and movement makes IR sensors indispensable in today’s automated and technology-driven world.
Can IR sensor detect Colour?
No, an IR sensor cannot detect color. Its primary function is to measure infrared radiation beyond the visible light spectrum. This limitation means it can detect objects’ presence, distance, and movement but not their color. However, this doesn’t diminish the IR sensor module’s utility in security and automation.
What are the 3 pins of an IR sensor?
The three pins of an IR sensor typically include the VCC (Voltage Common Collector), GND (Ground), and OUT (Output). VCC is for power input, GND is the ground connection, and OUT is the signal output that changes based on infrared light detection.
What are the different types of IR sensors?
There are two main types of IR sensors: Active and passive. Active IR sensors emit and detect infrared light using a transmitter and receiver. Passive IR sensors, on the other hand, only detect infrared radiation emitted from objects in their field of view without emitting any.
What are IR detectors used for?
Users employ IR detectors for various applications, including motion detection, obstacle detection, measurement of heat emissions, remote control technology, and line-following in robotics. They are essential in systems requiring non-contact detection of objects and their properties.
What is the full form of IR?
The full form of IR is Infrared. Infrared is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than radio waves. It is commonly used in various technologies, including sensors, to detect heat and movement.
Is IR sensor digital or analog?
IR sensors come in both digital and analog varieties. Digital IR sensors provide binary outputs, indicating the presence or absence of an object. In contrast, analog sensors offer a continuous signal that varies with the intensity of detected infrared radiation. This flexibility makes the IR sensor module adaptable for various applications, from simple presence detection to complex distance measuring.
How to connect IR sensor to Raspberry Pi?
Connecting an IR sensor to a Raspberry Pi involves a few straightforward steps. First, identify the sensor’s pins, typically ground, power, and signal. Connect these to the corresponding GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi. After establishing the physical connection, configure the Raspberry Pi’s software to read the sensor’s output, enabling it to interpret the IR sensor’s signals effectively. This setup is a gateway to numerous creative and practical applications in electronics and robotics.



