In a world increasingly driven by technology, the Infrared Sensor, or IR Sensor, emerges as a pivotal component in numerous applications. This guide embarks on an exploratory journey into the essence of IR Sensors. It unravels their fundamental nature and their critical role in modern technological advancements. IR Sensors have become an indispensable part of our technological landscape, from simplifying everyday tasks to enabling complex machinery. As we delve into their intricacies, we discover how they function and shape the interaction between technology and our daily lives. Check our other article, IR Sensor Working – Learn Every What and How of IR Sensor on vayuyaan.
What is an IR Sensor?
An Infrared Sensor, commonly known as an IR Sensor, is a pivotal component in modern technology, particularly sensor systems. Fundamentally, it’s a device that uses infrared light to detect and measure various aspects of its environment. By emitting or detecting infrared radiation, these sensors can perceive the physical world in ways beyond human capabilities. Our store offers an infrared sensor that’s easy to use. This sensor can help you detect heat and motion in your projects.
Why are they so crucial today? IR Sensors play an integral role in many applications, from the simplicity of remote controls to the complexities of industrial automation. They offer a non-intrusive, reliable means of sensing movement, measuring heat, and even determining the presence of particular objects. Their ability to work in environments where other sensors might fail makes them indispensable in today’s tech-driven world.
Working Principle of IR Sensors
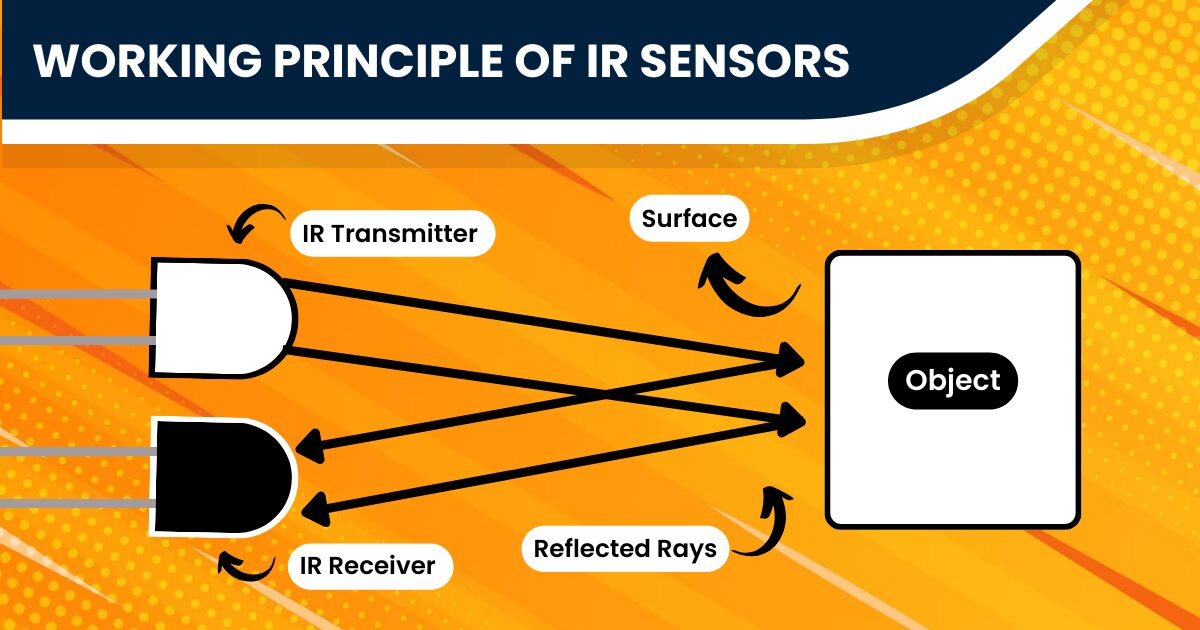
At the heart of an IR Sensor’s functionality are the IR LED and the Photodiode. The IR LED emits infrared light, which gets reflected upon hitting an object and is detected by the Photodiode. This simple yet effective mechanism enables an IR Sensor to perform its task. Discover everything about the IR Sensor Module – Infrared Sensor Complete Guide. Learn more in our other blog for easy, comprehensive insights.
However, not all IR Sensors are created equal. There are two main types: Active and Passive IR Sensors. Active IR Sensors are the more interactive ones. They emit infrared light and detect its reflection, making them perfect for applications requiring direct measurement. On the other hand, Passive IR Sensors are often used in security systems. They work by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by warm objects like human bodies.
Active IR Sensors create and detect signals. In contrast, Passive IR Sensors quietly observe and pick up infrared energy. This difference leads to diverse applications. Active IR Sensors excel in targeted detection, while Passive IR Sensors are preferred for surveillance and motion detection.
Types of IR Sensors and Their Uses
When delving into IR sensors, it’s crucial to grasp the diversity they offer. These sensors come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and needs. The range of choices from active to passive IR sensors can seem bewildering, but understanding their characteristics is crucial in selecting the right one for your project. Active IR sensors can emit and detect infrared light and find their home in precision-critical tasks. On the other hand, passive IR sensors, which rely on the naturally emitted infrared radiation from warm objects, excel in motion detection and presence sensing applications. Whether designing a robotic system, securing your home, or developing consumer electronics, knowing the different types of IR sensors available empowers you to make informed choices and harness their capabilities effectively.
Active IR Sensors
Active IR sensors are the cornerstone of precision in the sensor technology landscape. These sensors operate by emitting a beam of infrared light, which reflects off objects and returns to the sensor. This mechanism allows for exceptionally accurate object detection, making them indispensable in applications requiring high precision. For instance, active IR sensors reliably detect and count products in automated manufacturing lines, ensuring efficiency and accuracy. Moreover, in consumer electronics, they enhance user experience by enabling remote control of devices like TVs and air conditioners. Their ability to measure distances makes them invaluable in robotics, aiding navigation and obstacle avoidance.
Passive IR Sensors
Passive IR Sensors, a marvel in sensor technology, stand out for their ability to detect natural infrared radiation emitted by objects. Unlike their active counterparts, these sensors do not emit any infrared light; instead, they are finely tuned to sense the subtle infrared energy naturally given off, especially by warm objects like the human body. This unique capability makes them incredibly useful in various applications. For instance, in home security systems, passive IR sensors provide a reliable and non-intrusive way to detect potential intruders by sensing body heat.
Furthermore, they find extensive use in energy-saving applications like automated lighting systems. Lights activate upon detecting the human presence, favouring passive IR sensors in residential and commercial settings. This non-invasive tech improves safety, convenience, and energy conservation, harmonizing functionality with eco-friendliness.
Real-World Applications: Bringing Theory to Life
Infrared sensors, both active and passive, have carved their niche in various fields. Home security systems, for instance, leverage passive IR sensors for motion detection, offering an efficient and discreet security solution. In industrial settings, active IR sensors play a pivotal role in assembly lines, automating processes by detecting the presence and position of objects. They are also a key component in many consumer electronics, like television remote controls, which enable wireless communication between the remote and the TV.
Active vs Passive IR Sensors
The key lies in their operational mechanisms and specific applications when distinguishing between active and passive IR sensors. Active IR sensors, characterized by their proactive approach, emit infrared light, which, upon striking an object, is reflected and captured by the sensor. This active engagement makes them ideal for precise distance measurement and object detection, frequently utilized in automation processes and electronic devices like automatic faucets and barcode scanners.
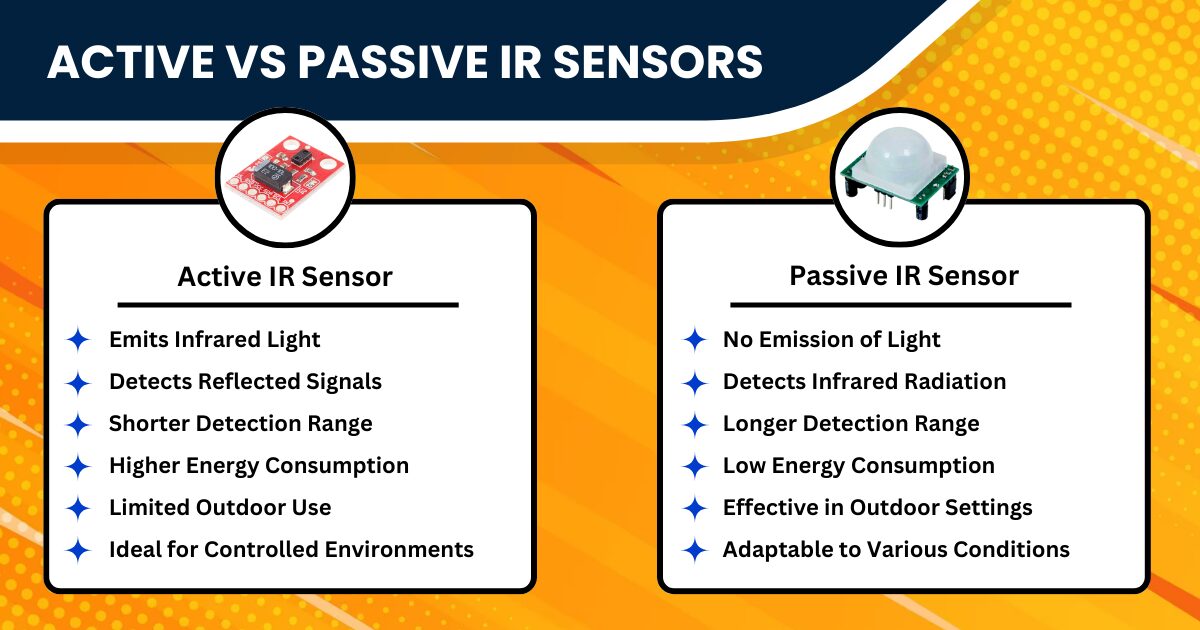
Conversely, passive IR sensors, operating more subtly, detect the infrared radiation naturally emitted by warm objects, such as humans or animals. This passive detection method makes them perfect for applications requiring motion sensing without direct interaction, such as security alarms and automatic lighting systems. Thus, while active IR sensors excel in tasks demanding dynamic interaction and precision, passive IR sensors are the preferred choice in scenarios where detecting presence or movement is crucial, without the need for emitted light. This detailed comparison highlights their unique roles and specific uses in various technological applications, showcasing their significance in modern sensor technology.
Specific Uses and Applications
In real-world scenarios, these differences translate into distinct applications. Active IR sensors are used in applications where accuracy and control are paramount. For example, in robotics, they aid in navigation and object detection, while in consumer electronics, they facilitate user-device interaction. Passive IR sensors, equipped to detect thermal signatures, play a fundamental role in security systems. They operate by automatically activating alarms or illumination systems when they sense the presence of a human being.
Design and Components of an IR Sensor
Exploring the design of an IR Sensor reveals a masterful integration of components, each serving a distinct purpose. Central to its functionality is the IR LED, which emits infrared light, forming the core of the sensor’s detection capability. This light, invisible to the naked eye, is the key to the sensor’s operation. Accompanying the IR LED is the Photodiode, a sensitive element that detects the IR light and converts it into an electrical signal. The precision and responsiveness of these components dictate the overall efficiency and range of the sensor, making their quality paramount.
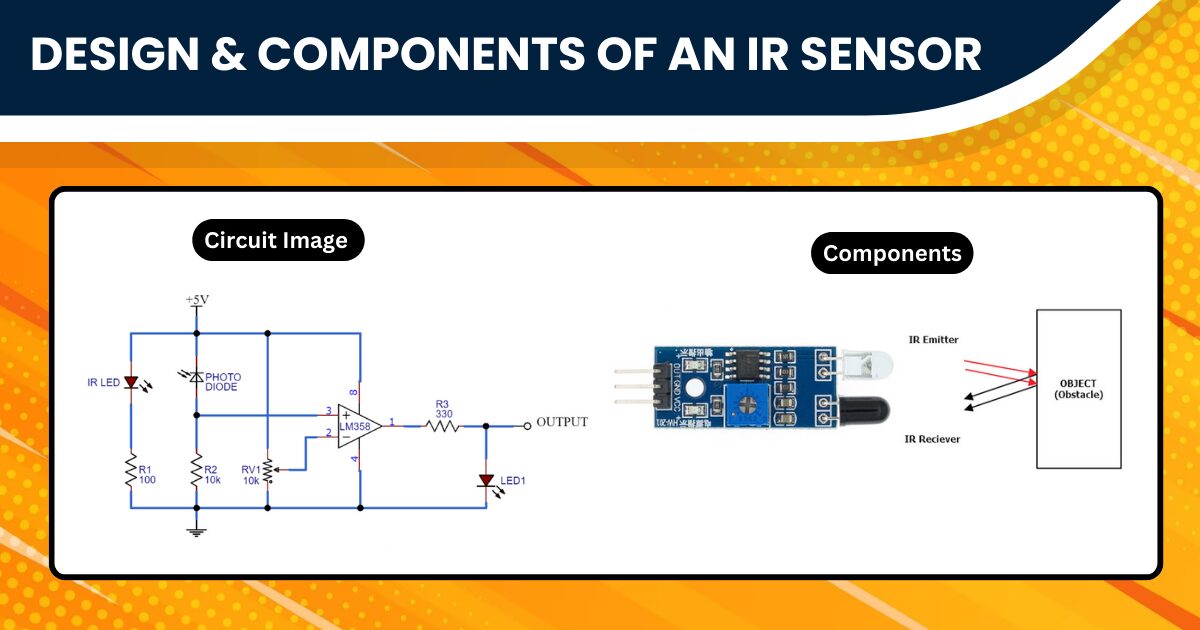
Additionally, the circuit board integrates resistors and capacitors, often accompanied by a potentiometer for adjusting sensitivity. This carefully crafted ensemble of components ensures the accurate detection of IR light. It makes the sensor versatile in various applications, from simple DIY projects to complex industrial systems. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone looking to harness the full potential of IR sensor technology in their endeavours.
IR LED: The Beacon of Infrared Light
The IR LED in an IR Sensor acts as a beacon, emitting infrared light. This invisible yet powerful light forms the basis of the sensor’s detection capabilities. The choice of IR LED impacts the IR sensor range, which can vary significantly based on the application.
Photodiode: The Unsung Hero
Complementing the IR LED is the Photodiode, a component sensitive to the IR light emitted. This sensitivity allows the IR Sensor to detect environmental changes, translating them into electrical signals. The precision of the Photodiode dictates the IR sensor detection range, making it a cornerstone of the module’s efficiency.
Circuitry and Connectivity
Beyond these two, the IR sensor circuitry weaves together various other components. Resistors, capacitors, and sometimes a potentiometer for adjusting sensitivity all find their place on the sensor’s board. Each element plays its role, ensuring that the IR sensor module works seamlessly with digital or analogue systems.
Installation and Calibration of IR Sensors
Installing an IR Sensor is a straightforward yet crucial task, pivotal to its accurate functioning. Begin by identifying an optimal location, ensuring minimal interference and maximum effectiveness. This placement is especially vital for applications requiring precise IR sensor range detection. Connect the essential pins – GND, Vcc, and Signal – carefully, adhering to the IR sensor module’s datasheet for guidance. This meticulous connection process lays the groundwork for reliable sensor performance.
To transition to calibration, you can fine-tune your IR Sensor to the nuances of its environment. Adjusting the potentiometer, a component often found in these sensors, allows you to modify the sensitivity, tailoring it to the specific requirements of your project. Precise calibration, whether adjusting the IR sensor range in meters for a security system or fine-tuning for a delicate experimental setup, is critical. Moreover, regular checks and recalibrations ensure that your sensor maintains its accuracy over time, adapting to changes in the surrounding conditions.
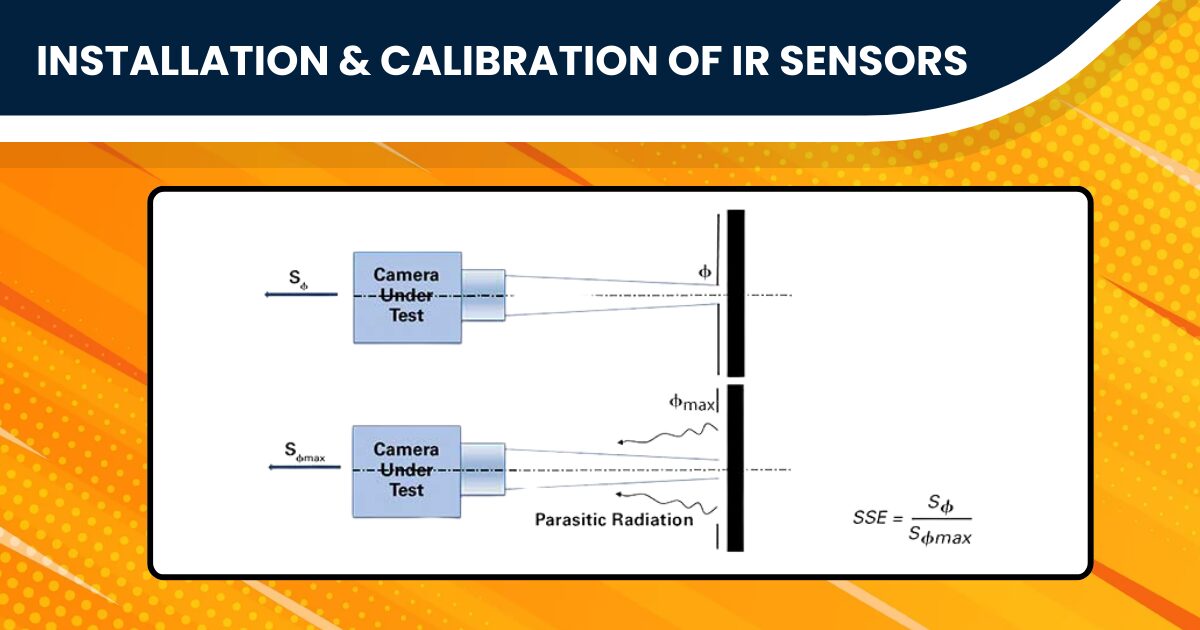
To summarise, effectively installing and calibrating an IR Sensor ensures optimal performance in diverse applications. Together with regular maintenance, this ensures its reliability in your tech toolkit.
Troubleshooting: Keeping Your Sensor in Top Shape
Facing issues with your IR Sensor can be challenging, but ensuring longevity and reliability through effective troubleshooting is essential. Inspect the connections, as loose wires or incorrect hookups are common culprits behind malfunctions. Refer to the IR sensor datasheet for precise troubleshooting guidance, as it is an invaluable resource. Furthermore, validate the power supply and thoroughly examine the sensor for any signs of physical damage. Simple solutions such as potentiometer adjustments or sensor surface cleaning can restore its performance. By incorporating regular maintenance and following these troubleshooting tips, you can keep your IR Sensor in optimal condition, ensuring it’s always ready for any application.
IR Sensor in Everyday Life
IR sensors, pivotal in modern technology, have transformed everyday gadgets, making them more user-friendly and efficient. For instance, remote controls for televisions and air conditioners rely on these sensors for seamless operation, simplifying user interaction. Additionally, many smartphones now incorporate IR sensors, enhancing features like facial recognition and proximity sensing. These sensors play a crucial role in energy conservation through automated lighting systems in home automation. They also bolster home security by detecting movements, contributing significantly to convenience and safety in our daily lives.
Consumer Electronics Featuring IR Sensors
IR sensors have become indispensable in various household gadgets. Remote controls, for instance, utilize IR sensors for seamless communication with televisions, air conditioners, and other appliances. By simply pressing a button, the IR sensor in the remote transmits signals, allowing for effortless control. Furthermore, many smartphones incorporate IR sensors to enable features like face recognition and proximity sensing, significantly boosting security and functionality.
IR Sensors in Home Automation and Security Systems
Home automation systems leverage IR sensors to create more innovative, efficient living spaces. For example, automated lighting systems use IR sensors to detect human presence, automatically turning lights on or off, thus conserving energy. Similarly, security systems employ IR sensors for motion detection, which is crucial in home safety. These sensors can detect intruders by sensing the infrared radiation emitted by a person, triggering alarms and notifying homeowners. IR Sensors are changing the way we protect our homes. Learn more about this in our other blog on how IR Sensors Revolutionizing Home Security Systems.
Advanced Applications of IR Sensors
In the realm of advanced technology, IR sensors are making remarkable strides. In industrial settings, they are indispensable for safely detecting gas leaks with precision and reliability. Furthermore, IR sensors have revolutionised environmental monitoring, adeptly identifying air pollutants and aiding in ecological conservation. In healthcare, their impact is profound; IR sensors facilitate non-contact temperature measurements, ensuring hygiene and patient comfort. They also play a pivotal role in medical research, with IR imaging techniques providing crucial insights into various health conditions. This cutting-edge application of IR sensors exemplifies their transformative role across diverse sectors, showcasing their versatility and importance.
Industrial and Environmental Monitoring
IR sensors play a vital role in maintaining safety and efficiency in the industrial sector. They detect gas leaks with precision, preventing potential hazards in facilities. Furthermore, these sensors are instrumental in environmental monitoring. They track air quality by identifying pollutants, contributing significantly to environmental conservation efforts. This application of IR sensors underscores their importance in safeguarding both industry operations and our natural surroundings. Their reliability and accuracy make them indispensable in these critical fields, showcasing the broad impact of IR technology in diverse domains.
Innovative Uses in Healthcare and Research
IR sensors unveil groundbreaking applications in the healthcare sector, profoundly impacting diagnostics and research. These sensors, integral in non-contact thermometers, offer quick and hygienic temperature readings, vital for patient care. Moreover, IR imaging sheds light on diverse health conditions in medical research by visualizing body heat patterns, opening new avenues for diagnosis and treatment. The innovative use of IR sensors boosts patient safety and advances medical research, showcasing their transformative role in healthcare. Their ability to deliver precise and non-invasive solutions underscores the sensor’s value in advancing medical science.
Choosing the Right IR Sensor
Selecting the ideal IR Sensor for your project or application hinges on understanding various factors and precisely interpreting specifications. Let’s delve into the crucial aspects to consider.
- Understanding Your Needs: Before diving into specifications, clearly define what you need the IR sensor for. The choice varies significantly, Whether for a simple DIY project, industrial application, or part of a sophisticated electronic device.
- Sensor Range and Sensitivity: One of the primary considerations is the IR sensor range, typically measured in meters or centimetres. The range you need depends on how far the sensor must detect infrared radiation. Furthermore, sensitivity plays a crucial role, especially in applications where detecting subtle changes is vital.
- Types and Applications: Various types of IR sensors, such as active and passive, serve different purposes. For instance, active IR sensors, known for their emitter-detector setup, are ideal for precise short-range detection. Conversely, passive IR sensors, detecting emitted IR radiation, suit applications like motion detection.
- Interpreting Datasheets: Datasheets provide a wealth of information. Look for crucial specifications like the IR sensor range, power requirements (Vcc), and the signal output type. Understanding these details ensures you pick a sensor that matches your technical needs.
- Price and Availability: Consider the IR sensor price, ensuring it fits your budget while meeting quality standards. Availability is also crucial, especially for bulk or continuous supply needs.
- Compatibility and Integration: Ensure the IR sensor is compatible with your existing setup, particularly the connection interface (analogue or digital) and voltage requirements.
Future Trends in IR Sensor Technology
The horizon of IR Sensor technology brims with innovations and potential impacts that promise to revolutionize various sectors.
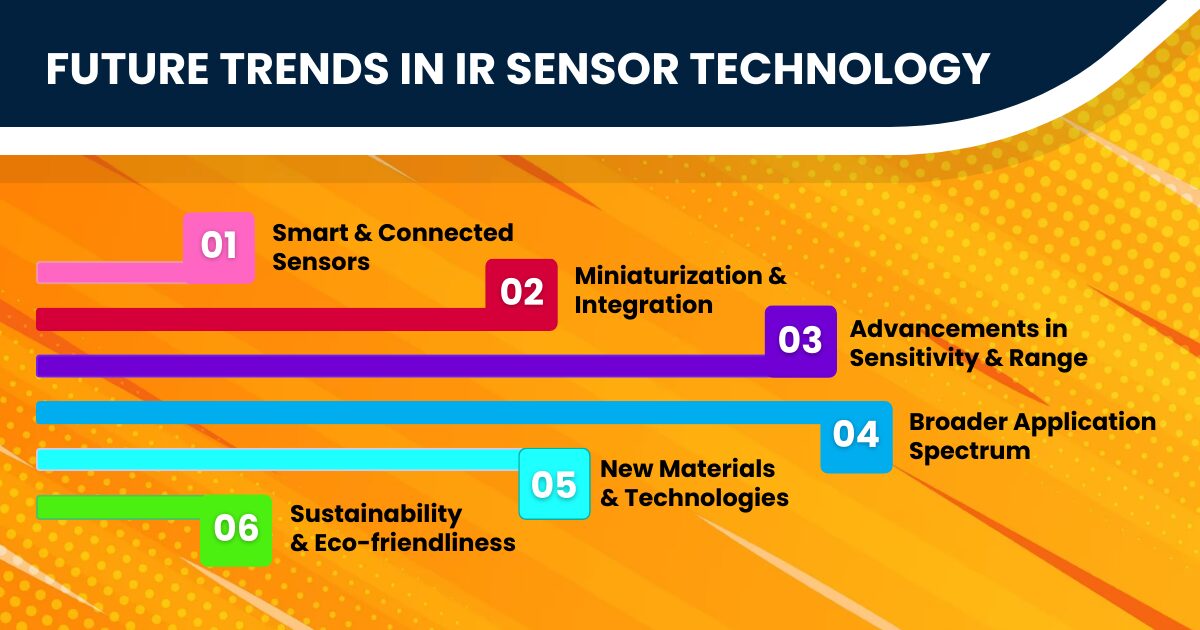
- Advancements in Sensitivity and Range: Researchers continually push the boundaries of how sensitive and far-reaching IR sensors can be. This progress paves the way for more precise and efficient sensors, enhancing applications from environmental monitoring to security systems.
- Miniaturization and Integration: The trend towards smaller, more integrated sensors aligns with the growing demand for compact and mobile devices. This miniaturization does not only make IR sensors more versatile but also more affordable.
- Smart and Connected Sensors: Integrating IR sensors with IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) technologies is a game-changer. Smart IR sensors, capable of analyzing data and making decisions, are set to transform industries by enabling more autonomous and responsive systems.
- New Materials and Technologies: Explorations into novel materials and technologies, like graphene-based IR sensors, open up possibilities for improved performance, including faster response times and greater durability.
- Broader Application Spectrum: From healthcare, where IR sensors are used in non-invasive diagnostics, to automotive safety improvements and smart home applications, the scope of IR sensor applications is expanding rapidly.
- Sustainability and Eco-friendliness: Future IR sensor development also focuses on sustainability. Eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs are becoming increasingly important.
Conclusion
In our exploration of IR Sensors, we recognize that these devices transcend mere electronic components. They serve as unsung heroes across diverse applications, from bolstering home security to transforming industrial processes. The adaptability of IR sensors, spanning from basic hobbyist modules to sophisticated healthcare systems, underscores their significance in our tech-driven world.
As we reflect on our journey, we can distil critical takeaways that encompass the fundamental principles of IR sensors, explore the distinction between active and passive types, and appreciate their broad applications. Whether in consumer electronics, detecting remote control signals, or advanced domains like environmental monitoring and healthcare, IR sensors continue to expand their horizons.

The future of IR sensor technology holds great promise, fueled by advances in materials and electronics. Expect more efficient, sensitive, and compact sensors, opening doors to innovation in areas like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Therefore, enthusiasts, professionals, and innovators need to stay well-informed about these advancements. Embracing IR sensors’ potential and exploring their capabilities can lead to groundbreaking applications yet unimagined. As we delve deeper into their possibilities, let us honour their humble origins—a simple yet transformative tool shaping our tech landscape.
In conclusion, IR sensors, with their diverse applications and evolving tech, are a testament to human ingenuity and relentless progress. We encourage continued exploration and innovation in this field, holding the key to unlocking remarkable technological feats. Let curiosity thrive as we explore IR sensors’ vast potential in shaping a more innovative, more efficient world.



